Aerial shot of Middleton Reef, Lord Howe Island
Black-tip reef shark (Carcharhinus melanopterus) swims above the coral at Blue Hole, Middleton Reef during a Reef Life Survey dive.
Galapagos sharks are abundant in the Lord Howe Marine Park and play an important role as an apex predator
Fishers are coming into conflict with Galapagos sharks because the sharks often take hooked fish before they can be retrieved to the boat, a process called depredation.
Istigobius decoratus, known as the Decorated Sandgoby is found on sand patches near reefs.
 by Ian Shaw
by Ian Shaw by University of Western Australia
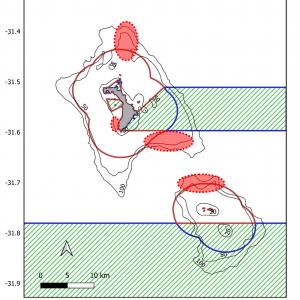
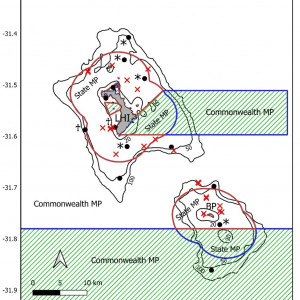
by University of Western AustraliaDetailed map showing acoustic receiver locations (black circles) and shark tagging locations (red crosses). Solid dark red lines show the boundaries of the Lord Howe MP (Commonwealth waters) and the Lord Howe Island Marine Park (NSW waters). No-take zones are marked with hashed green lines. Solid black lines indicate the 20, 50 and 100m depth contours. Key: LHI = Lord Howe Island, BP = Ball’s Pyramid
* denotes receivers which were only deployed between January 2018 and January 2019
♰ indicates receivers which were deployed from January 2019 to January 2021. by University of Western Australia
by University of Western AustraliaReef Life Survey diver at Middleton Reef, Lord Howe Marine Park.
 by Reef Life Survey
by Reef Life SurveySchool of Moorish idols (Zanclus cornutus) as recorded on Reef Life Survey volunteer transect, Lord Howe Island Marine Park, New South Wales. The Reef Life Survey program is a volunteer network of highly trained divers, and is a product of the CERF Major Projects funding that facilitated a cost-effective citizen science contribution to inventory and monitoring of shallow water marine environments. The RLS program has been further facilitated within the NERP Hub, describing biodiversity patterns at a national and global scale, as well as providing critical baseline data from areas such as the new Coral Sea Marine Park, from Ashmore Reef, the Great Barrier Reef,and other Australian Marine Parks such as the Cod Grounds.
 by Reef Life Survey
by Reef Life SurveyPleurosicya mossambica also known as the toothy goby or the Mozambique ghost goby is found on many substrates, including corals, sponges, giant clams and seaweeds, and can vary colour according to the substrate.
 by Ian Shaw
by Ian ShawReef Life Survey (RLS) diver conducts visual census of reef biodiversity at Elizabeth Reef using standardised RLS methods as part of a collaborative survey expedition with James Cook University (JCU) and Parks Australia
Reef Life Survey volunteer swimming along 50 metre transect recording fish diversity and abundance. The Reef Life Survey program is a volunteer network of highly trained divers, and is a product of the CERF Major Projects funding that facilitated a cost-effective citizen science contribution to inventory and monitoring of shallow water marine environments. The RLS program has been further facilitated within the NERP Hub, describing biodiversity patterns at a national and global scale, as well as providing critical baseline data from areas such as the Coral Sea Marine Park, from Ashmore Reef, the Great Barrier Reef,and other Australian Marine Parks such as the Cod Grounds.
 by Reef Life Survey
by Reef Life SurveyReef Life Survey volunteer diver conducting underwater visual census survey of marine life, Lord Howe Island Marine Park, New South Wales. The Reef Life Survey program is a volunteer network of highly trained divers, and is a product of the CERF Major Projects funding that facilitated a cost-effective citizen science contribution to inventory and monitoring of shallow water marine environments. The RLS program has been further facilitated within the NERP Hub, describing biodiversity patterns at a national and global scale, as well as providing critical baseline data from areas such as the new Coral Sea Marine Park, from Ashmore Reef, the Great Barrier Reef,and other Australian Marine Parks such as the Cod Grounds.
 by Reef Life Survey
by Reef Life Survey