Apollo Marine Park contains sediment ecosystems, deep (mesophotic) reefs and a 5m high raised ridge feature, suspected to be deeper (rariphotic) reef habitat extending from the western park boundary to the northern park boundary1. The park covers representative areas of five bioregions.
Knowledge status
Apollo Marine Park has a low to medium level of knowledge.
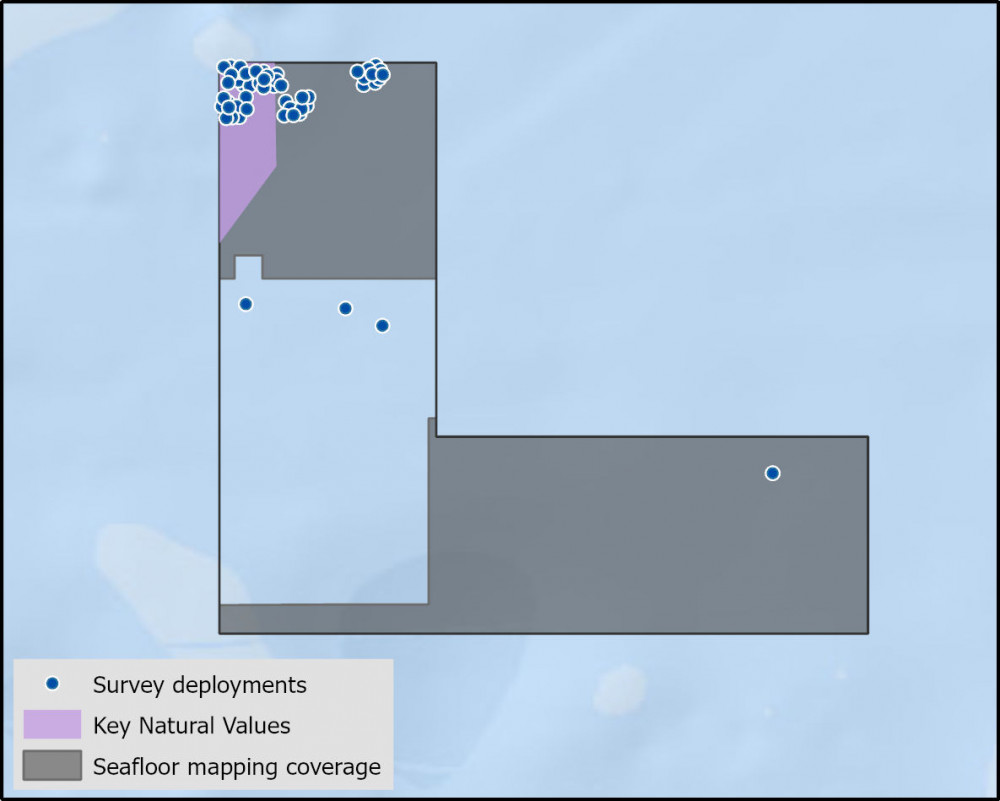
- Fine-scale mapping includes high biodiversity areas of deep (mesophotic) reef ecosystems in the northwest corner. This area has been a focus for fish community surveys, with data from 50 Baited Remote Underwater Video systems yet to be analysed. The southeast section of the park has also been mapped with interpretation of seabed features yet to be undertaken.
- There have been 50 video deployment over 1 campaign and 4 sediment samples collected from a single survey.
- There are 13 publications, reports and data sets that reference the South east network and relate to Apollo Marine Park as well as 4 publications that are specific to Apollo Marine Park.
- Depth: 47m – 101m
- 60% of seafloor mapped, most at medium to high resolution to support habitat mapping and biodiversity surveys.
Key values, habitats and communities
Seafloor mapping has uncovered extensive Mesophotic reefs of varying complexity in the northwest corner of the park, between approx. 45m and 70 m depth. The raised ridge feature, of 75-80m depth, extends from the western park boundary to the northern park boundary in a southwest - northeast direction1.

Feature of interest
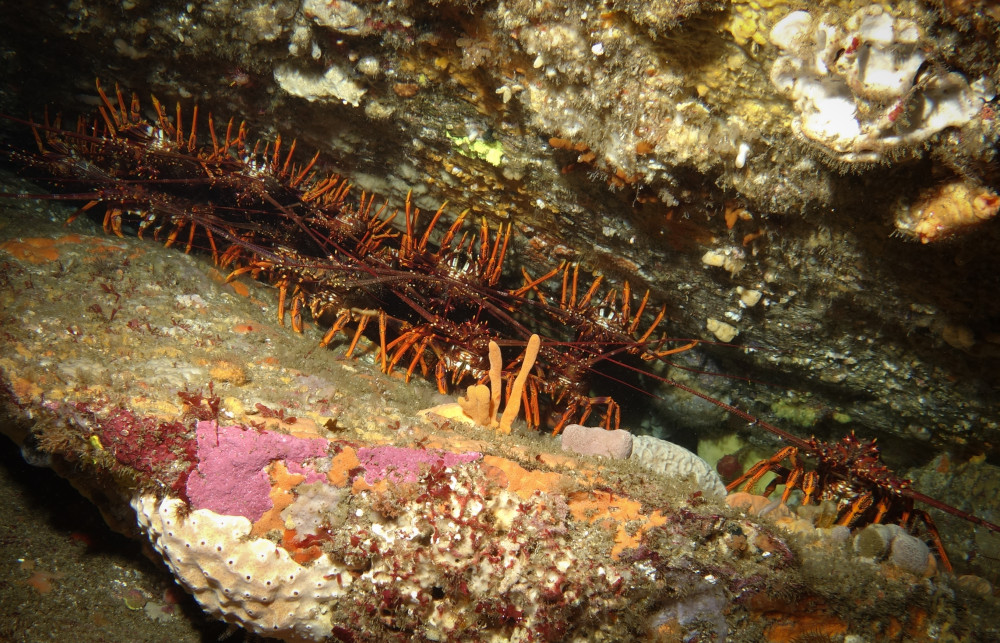
Southern rock lobsters are thought to migrate throughout the year between the highly productive state waters and Apollo Marine Park reef systems.
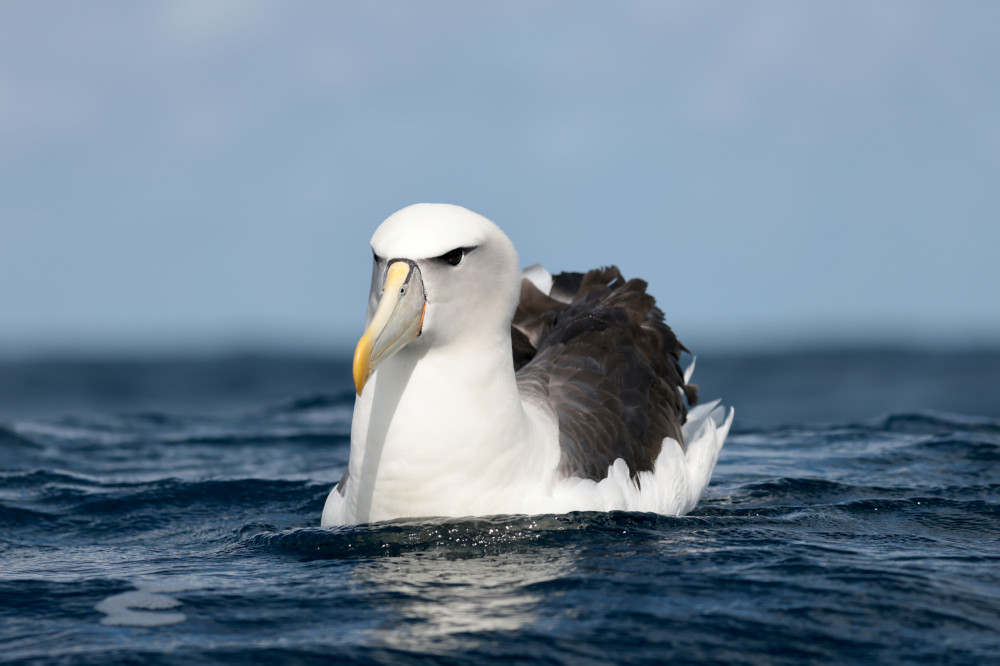
A rich diversity of oceanic seabirds forage in these waters, including the endangered Shy Albatross (Thalassarche cauta).

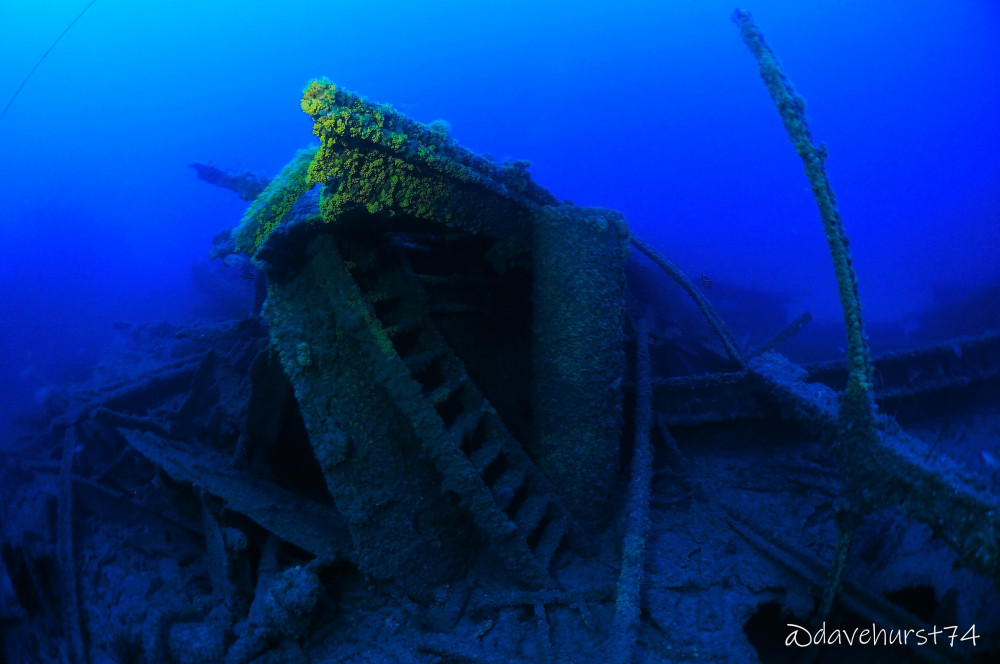
Known underwater cultural heritage3
The MV City of Rayville, an American motor ship, is located on the western side of Apollo Marine Park in 82m of water. It was the first American vessel sunk during World War Two, on the 8th of November 1940, after hitting a mine. The wreck was first surveyed in 2009 re surveyed in 2019 by Deakin University2.

Key gaps
- Deep (mesophotic and rariphotic) shelf reef benthic communities and demersal fish communities.
- Soft sediment benthic communities (epifauna and infauna) and contaminant levels (e.g. hydrocarbons, heavy metals).
Key activities
- Commercial fishing
- Recreational fishing
- Shipping
Key Pressures
- Resource extraction
- Climate change
- Underwater noise
Seafloor mapping and survey deployments
Further information:
State of Knowledge published Mar 2023 | References:
- Ierodiaconou D, Young M, O’Brien S (2020) Hydrographic Survey of Apollo Marine Park. Final report to Parks Australia, Warrnambool, May. CC BY 4.0
- Deakin (2009) (https://www.deakin.edu.au/about-deakin/news-and-media-releases/articles/2009/world-war-ii-wreck-revealed).
- Protected under the Underwater Cultural Heritage Act 2018 (UCH) and included on the National and Commonwealth Heritage Lists under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC Act).
Key Natural Values (KNV) = Habitat or species that are particularly important to management.
Printable version: AMP - SE SOK Placemat templates (parksaustralia.gov.au)